Flatsat Overview

FlatSat Overview
A FlatSat is a ground-based, test-ready version of a satellite with all its components laid out on a table rather than in a compact structure. This configuration allows for direct access to each subsystem, facilitating testing and troubleshooting in a controlled lab environment.
Purpose and Use
FlatSats are used primarily to test satellite systems and their interoperability before launch, ensuring each component functions correctly. This setup supports end-to-end operations as if in orbit, allowing for command and telemetry testing. For CubeSats, FlatSats provide a low-cost, modular test environment suitable for educational purposes, commercial applications, and experimental payloads.
Typical Components
A FlatSat for CubeSat might include: - On-Board Computer (OBC) - Power System - Telemetry and Radio System - Attitude Determination and Control System (ADCS) - Navigation Receiver
Additional slots are often available for custom hardware or experimental components, such as AI-based detection algorithms or radiation monitoring payloads.
Advantages
- Accessibility: Subsystems are physically separated, making them accessible for individual testing and replacement.
- Operational Simulation: Commands can be sent via a simulated ground station, with telemetry received for analysis.
- Flexibility: Engineers can easily swap or modify components, an asset for educational and fast-paced commercial projects.
- Testing New Technologies: Allows for validation of new components like radiation-tolerant microcontrollers in a representative environment.
Endurance Flatsat
Ressources
Endurance data handling architecture
To describe the different components of the flatsat planned for Endurance, I’m using the DHS view, which allows me to outline the communication protocols between the various systems.
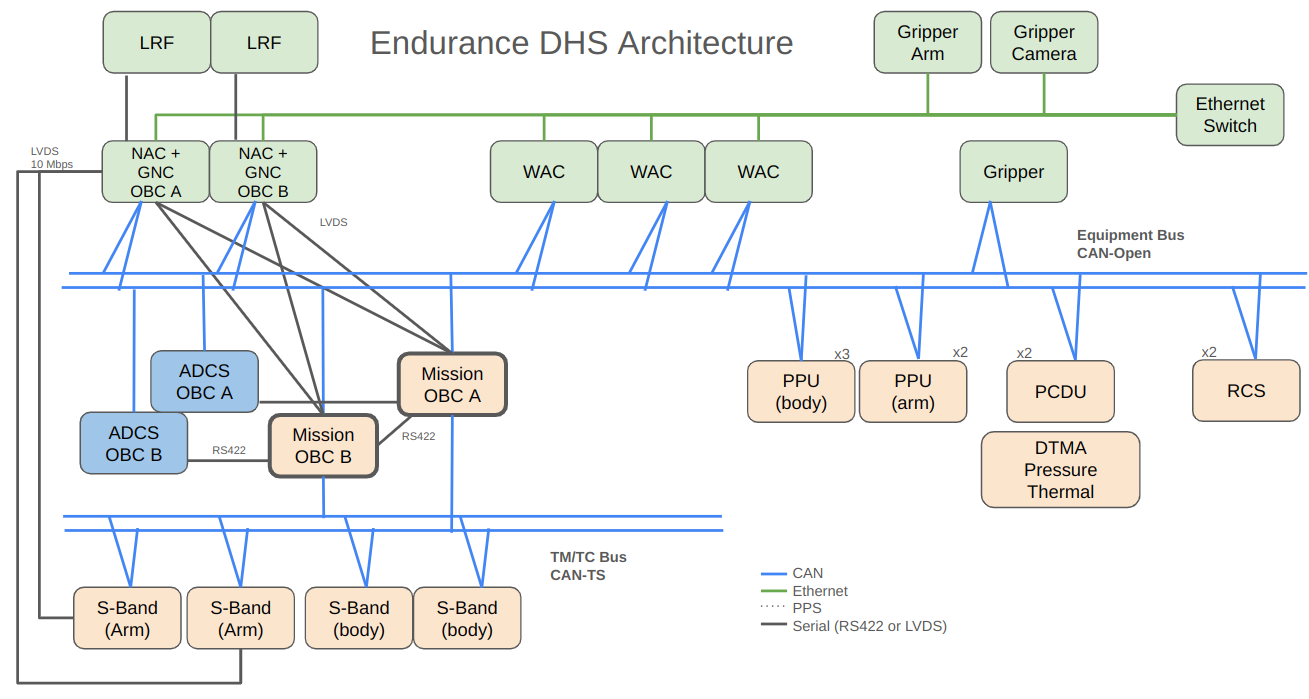
The flatsat includes:
- Flight software
- Two mission onboard computers (OBCs) in warm redundancy to manage AOCS (orbit), PU, Com, Th, and equipment
- Ground segment software (Yamcs) for communication with the OBC
- EGSE for pre-launch spacecraft testing and simulation
- Flatsat computer
- Simulation software
- Power supply
Note: Mission OBCs differ from guidance, navigation, and control (GNC) OBCs (Rendezvous & Grippers) and attitude (ADCS) OBCs, which are also in warm redundancy pairs.
This architecture contains 3 main networks :
- Best effort Ethernet
- CAN-TS
- CAN-Open
It also contains point to point communications through LVDS and RS422
